Project structure
GitHub
Below is the project solution structure
- .gitattributes
- .gitignore
- .gitlab-ci.yml
- Batch.File.Executor.sln
- Batch.File.Executor.sln.DotSettings.user
- LICENSE.txt
- README.md
DirectoryBatch.File.Executor # WinForms project
- Batch.File.Executor.csproj
- Batch.File.Executor.csproj.user
- editor.html
DirectoryMainForm.cs
- MainForm.Designer.cs
- MainForm.resx
- NLog.config
- Program.cs
DirectoryControllers
- AppControllerBase.cs
- BatchFileAppController.cs
- ExecuteFileController.cs
- LogController.cs
- Lib
DirectoryMonaco
- … # library comes here
DirectoryModels
- Datamodel.cs
DirectoryProperties
DirectoryPublishProfiles
- FolderProfile.pubxml
- FolderProfile.pubxml.user
- Resources
- $this.Icon.ico
DirectoryService
- AppLogger.cs
DirectoryUserControls
DirectoryMainView.cs
- MainView.Designer.cs
- MainView.resx
DirectoryViews
DirectoryDialogBase.cs
- DialogBase.Designer.cs
- DialogBase.resx
DirectoryDialogNewFile.cs
- DialogNewFile.Designer.cs
- DialogNewFile.resx
DirectoryDialogUpload.cs
- DialogUpload.Designer.cs
- DialogUpload.resx
DirectoryUnit.Tests # Tests
- Database_Reset.cs
- NLog.config
- Test_EF_Database.cs
- Test_Execution.cs
- Test_NLog.cs
- Unit.Tests.csproj
DirectoryModels
- Datamodel.cs
Application setup
- Create a Windows Forms C# project in visual studio
- Create also a Unit Test project
Nuget Packages
-
Packages for
Windows Forms C#project- FontAwesome.Sharp (6.6.0)
- Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore (8.0.8)
- Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Sqlite (8.0.8)
- Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Tools (8.0.8)
- Microsoft.Web.WebView2 (1.0.2739.15)
- NLog (5.3.3)
- NLog.Databases (5.3.3)
- NLog.Extensions.Logging (5.3.12)
- System.Data.SQLite (1.0.118)
-
Packages for
Unit Testproject- coverlet.collector (6.0.2)
- Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore (8.0.8)
- Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.InMemory (8.0.8)
- Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Tools (8.0.8)
- Microsoft.Web.WebView2 (1.0.2739.15)
- NLog (5.3.3)
- NLog.Databases (5.3.3)
- NLog.Extensions.Logging (5.3.12)
- System.Data.SQLite (1.0.118)
- xunit (2.9.0)
- xunit.runner.visualstudio (2.8.2)
Log configuration
In this project, the logging of system and user actions are saved to SQLite database and alternatively as files. To achieve this, we will be using NLog framework.
-
NLog internal configuration - for the logging framework itself
internalLogLevel- level of logging required for viewinginternalLogFile- location of theNLogLogging
-
Targetsin NLog define where the logs are to be sent. This could be console, file or even database. For this project, we are going to save the logs in file (maximum 4 files) and to SQLite database itself- For the file target,
layoutattribute defines how each line is formatted. - For the database target,
commandTextelement defines how each entry is saved to the database.parameterare defined in the command text, which then can have an element describing thelayout
- For the file target,
-
Rulesdefine which logger is allowed to write to the target. Logging granularity can be set with the attributeminlevel
Refer the entire configuration of the NLog below.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?><nlog xmlns="http://www.nlog-project.org/schemas/NLog.xsd" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" internalLogLevel="Debug" internalLogFile="c:\temp\nlog-internal.txt" internalLogToConsole="true" throwConfigExceptions="true" > <targets> <target name="file" xsi:type="File" layout="${longdate} | ${logger} | ${level:uppercase=true} | ${event-properties:item=batchFileId} | ${message}${exception:format=ToString}" fileName="C:/Temp/logs/AppLog.${shortdate}.txt" maxArchiveFiles="4" archiveAboveSize="10240" />
<target xsi:type="Database" name="database"> <dbProvider>System.Data.SQLite.SQLiteConnection, System.Data.SQLite</dbProvider> <connectionString>Data Source=batchfileexecutor.db;Version=3;</connectionString> <commandType>Text</commandType> <commandText> INSERT INTO Log (LogDate, Level, BatchFileId, Message) VALUES (@logdate, @level, @batchfileid, @message) </commandText>
<parameter name="@logdate" layout="${longdate:universalTime=true}" /> <parameter name="@level" layout="${level:uppercase=true}" /> <parameter name="@batchfileid" layout="${event-properties:item=BatchFileId}" /> <parameter name="@message" layout="${message}" />
</target>
</targets>
<rules> <logger name="*" minlevel="Trace" writeTo="database" /> <logger name="*" minlevel="Trace" writeTo="file" /> </rules></nlog>Important code snippets
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.Schema;using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
namespace Batch.File.Executor.Models;
[Table("BatchFile")]public class BatchFile{ public int Id { get; set; } public string display_name { get; set; } public DateTime created_at { get; set; } public DateTime? last_modified_at { get; set; } public string text { get; set; } public DateTime? last_executed_at { get; set; } public string? comment { get; set; }
public ICollection<ExecutionLog> ExecutionLogs { get; set; } = new List<ExecutionLog>(); public ICollection<Log> Logs { get; set; } = new List<Log>();}
[Table("ExecutionLog")]public class ExecutionLog{ public int Id { get; set; } public DateTime time_start { get; set; } public DateTime time_end { get; set; } public int BatchFileId { get; set; } public BatchFile BatchFile { get; set; }
public override string ToString() => $"Execution ID ({Id}): {time_start} - {time_end}";}[Table("Log")]public class Log{ public int Id { get; set; } public DateTime LogDate { get; set; } public string Level { get; set; } public string Message { get; set; } public int BatchFileId { get; set; } public BatchFile BatchFile { get; set; }}
public class LogItem(Log log){ public Log Log => log; public string FullMessasge => $"{Log.LogDate.ToLocalTime():yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss} [{Log.Level}] {Log.Message}"; public int Id => Log.Id;}
public class BatchFileExecutorContext : DbContext{ public BatchFileExecutorContext() { } public BatchFileExecutorContext(DbContextOptions<BatchFileExecutorContext> options) : base(options) { }
// Entities public DbSet<BatchFile> BatchFiles { get; set; } public DbSet<ExecutionLog> ExecutionLogs { get; set; } public DbSet<Log> Logs { get; set; }
// Connection Builder protected override void OnConfiguring(DbContextOptionsBuilder? optionsBuilder) { if (optionsBuilder is { IsConfigured: false }) { optionsBuilder.UseSqlite(@"Data Source=batchfileexecutor.db"); } }}using NLog;
namespace Batch.File.Executor.Service;
public class AppLogger{ private static readonly Logger Logger = LogManager.GetCurrentClassLogger();
public void Write(LogLevel logLevel, int batchFileId, string message) { var logEventInfo = new LogEventInfo(logLevel, Logger.Name, message) { Properties = { ["BatchFileId"] = batchFileId, } };
Logger.Log(logEventInfo); }}UI development
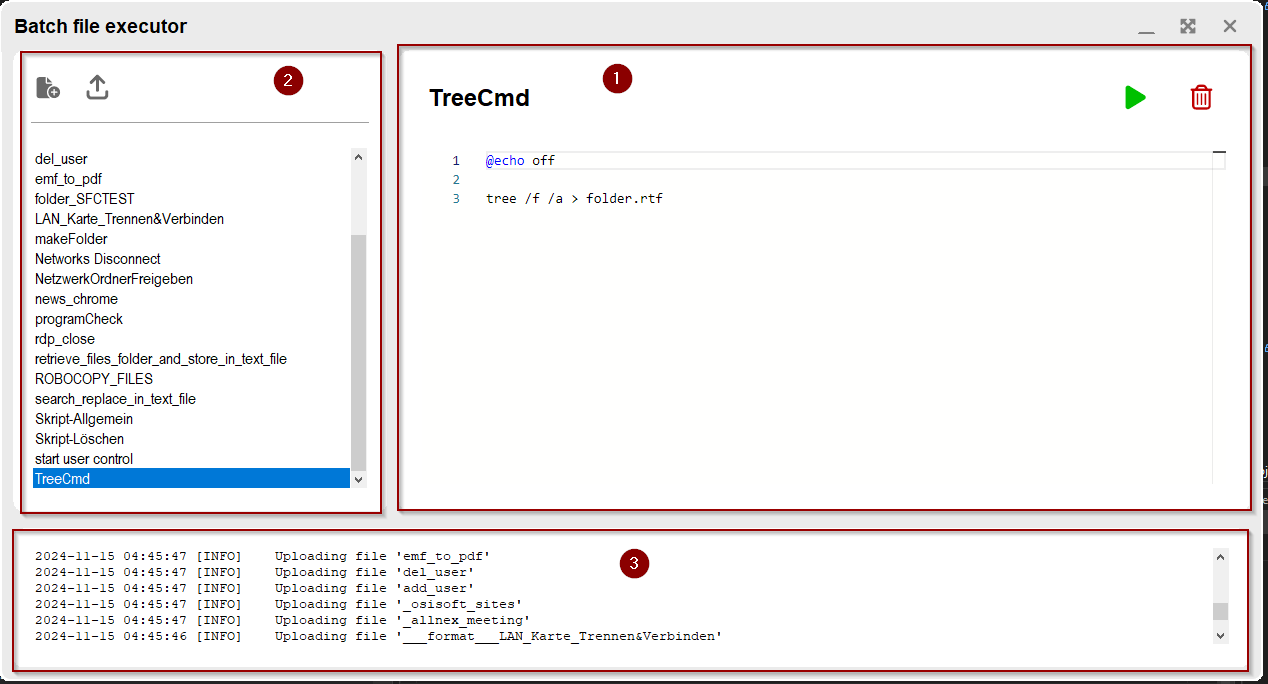
MainView- consist of the batch file along with start and delete buttonsSidebar- actions for create and uploading files, lists available batch files for ExecuteFileControllerLogger- displays the user and system action
Mainview
The main view consists of filename, start button and delete button.
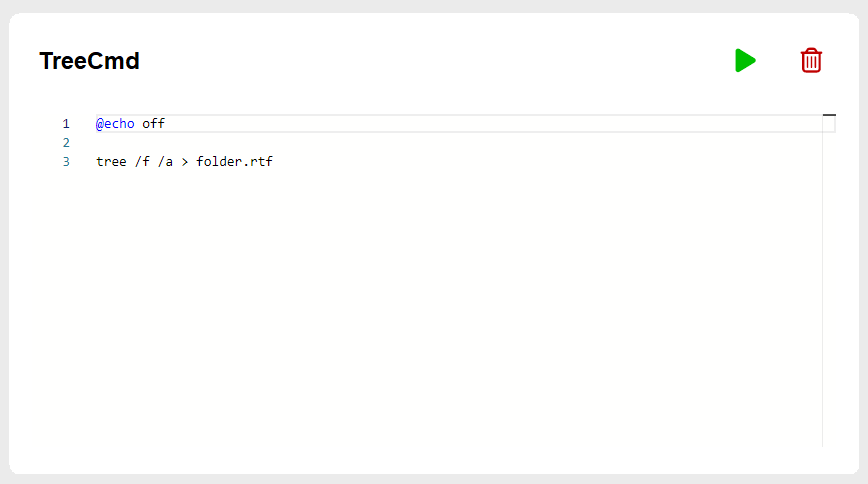
Check the tabs for the integration of Monaco editor which powers the VSCode.
#region Monaco Editor
// Method to set content dynamically in the Monaco Editor private async void SetEditorContent(string content) { // Execute JavaScript in the WebView2 to update the editor content var script = $"setEditorContent({EscapeJavaScriptString(content)});"; if (webView21.CoreWebView2 != null) await webView21.ExecuteScriptAsync(script); }
// Utility method to escape JavaScript strings to prevent errors private static string EscapeJavaScriptString(string s) { return "\"" + s.Replace("\\", "\\\\").Replace("\"", "\\\"").Replace("\n", "\\n").Replace("\r", "\\r") + "\""; }
private async void InitializeWebView2Async() { // Ensure WebView2 is ready before loading the content await webView21.EnsureCoreWebView2Async(null);
// Get the path of the HTML file containing the Monaco Editor var currentDirectory = Directory.GetCurrentDirectory(); var editorHtmlPath = Path.Combine(currentDirectory, "editor.html");
// Load the editor.html file into the WebView2 webView21.Source = new Uri(editorHtmlPath);
} #endregion<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>Monaco Editor</title> <style> body, html { margin: 0; padding: 0; width: 100%; height: 100%; overflow: hidden; }
#container { width: 100%; height: 100vh; } </style> <script src="Lib/Monaco/min/vs/loader.js"></script></head><body> <div id="container"></div> <script>
let editor; // Declare the editor variable globally
// Configure the path to the local Monaco Editor files require.config({ paths: { 'vs': 'Lib/Monaco/min/vs' } }); require(['vs/editor/editor.main'], function () { editor = monaco.editor.create(document.getElementById('container'), { value: [ 'loading...', ].join('\n'), language: 'bat', // Set language to Batch script minimap: { enabled: false }, // Hide the mini-map theme: 'vs-light', // vs-dark automaticLayout: true, wordWrap: "on", }); });
// Function to set content dynamically from C# function setEditorContent(content) { if (editor) { editor.setValue(content); } else { console.error("Editor is not initialized."); } } // Function to get the content of the Monaco Editor function getEditorContent() { return editor ? editor.getValue() : ''; } </script></body></html>#region Monaco Editor
// Method to set content dynamically in the Monaco Editorprivate async void SetEditorContent(string content){ // Execute JavaScript in the WebView2 to update the editor content var script = $"setEditorContent({EscapeJavaScriptString(content)});"; if (webView21.CoreWebView2 != null) await webView21.ExecuteScriptAsync(script);}
// Utility method to escape JavaScript strings to prevent errorsprivate static string EscapeJavaScriptString(string s){ return "\"" + s.Replace("\\", "\\\\").Replace("\"", "\\\"").Replace("\n", "\\n").Replace("\r", "\\r") + "\"";}
private async void InitializeWebView2Async(){ // Ensure WebView2 is ready before loading the content await webView21.EnsureCoreWebView2Async(null);
// Get the path of the HTML file containing the Monaco Editor var currentDirectory = Directory.GetCurrentDirectory(); var editorHtmlPath = Path.Combine(currentDirectory, "editor.html");
// Load the editor.html file into the WebView2 webView21.Source = new Uri(editorHtmlPath);
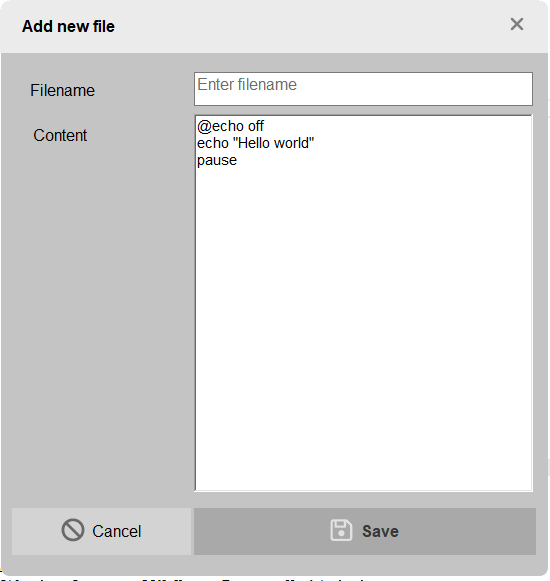
}#endregionDialogNewFile
DialogUpload
- Upload multiple files
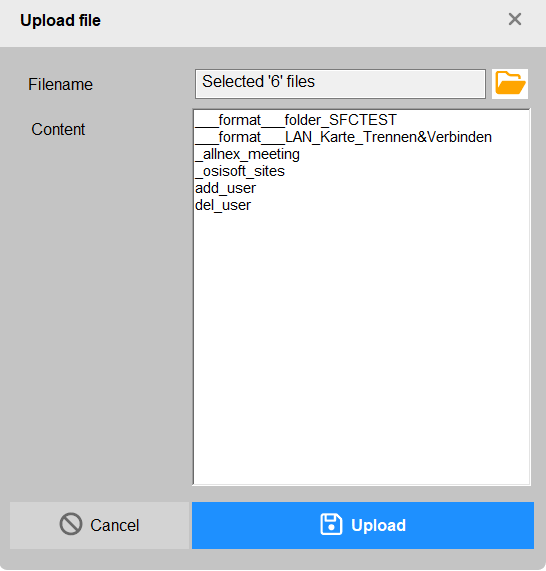
- Upload single file
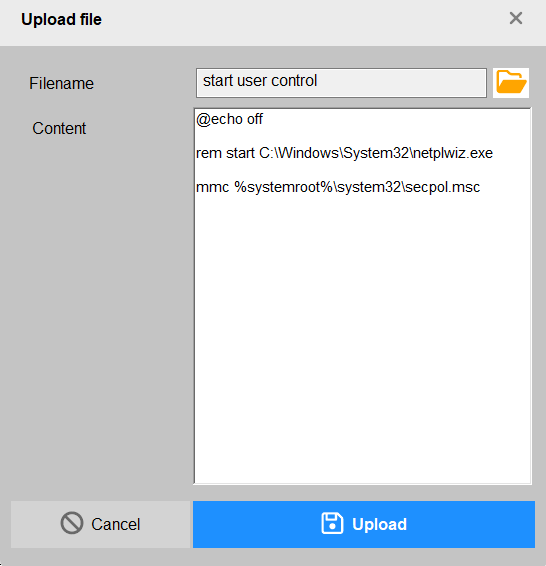
LoggerView

UI - titbits
Below I will show you essential code bits required to reproduce the Modern UI in Windows Forms.
Modern UI

In the MainForm.cs file,
private int borderRadius = 10; private int borderSize = 2; private Color borderColor = Color.White; private Color titlebarColor = Color.FromArgb(235, 235, 235); private Color containerColor = Color.FromArgb(235, 235, 235);
void SetIconColors(Button control, Color color) { control.BackColor = color; control.FlatAppearance.BorderColor = color; }#region curved border mainform and ui components//Drag Form[DllImport("user32.DLL", EntryPoint = "ReleaseCapture")]private extern static void ReleaseCapture();[DllImport("user32.DLL", EntryPoint = "SendMessage")]private extern static void SendMessage(System.IntPtr hWnd, int wMsg, int wParam, int lParam);
protected override CreateParams CreateParams{ get { CreateParams cp = base.CreateParams; cp.Style |= 0x20000; // <--- Minimize borderless form from taskbar return cp; }}
// Private methodsprivate GraphicsPath GetRoundedPath(Rectangle rect, float radius){ GraphicsPath path = new GraphicsPath(); float curveSize = radius * 2F;
path.StartFigure(); path.AddArc(rect.X, rect.Y, curveSize, curveSize, 180, 90); path.AddArc(rect.Right - curveSize, rect.Y, curveSize, curveSize, 270, 90); path.AddArc(rect.Right - curveSize, rect.Bottom - curveSize, curveSize, curveSize, 0, 90); path.AddArc(rect.X, rect.Bottom - curveSize, curveSize, curveSize, 90, 90); path.CloseFigure(); return path;}
private void FormRegionAndBorder(Form form, float radius, Graphics graph, Color borderColor, float borderSize){ if (this.WindowState != FormWindowState.Minimized) { using (GraphicsPath roundPath = GetRoundedPath(form.ClientRectangle, radius)) using (Pen penBorder = new Pen(borderColor, borderSize)) using (Matrix transform = new Matrix()) { graph.SmoothingMode = SmoothingMode.AntiAlias; form.Region = new Region(roundPath); if (borderSize >= 1) { Rectangle rect = form.ClientRectangle; float scaleX = 1.0F - ((borderSize + 1) / rect.Width); float scaleY = 1.0F - ((borderSize + 1) / rect.Height);
transform.Scale(scaleX, scaleY); transform.Translate(borderSize / 1.6F, borderSize / 1.6F);
graph.Transform = transform; graph.DrawPath(penBorder, roundPath); } } }}
private void ControlRegionAndBorder(Control control, float radius, Graphics graph, Color borderColor){ using GraphicsPath roundPath = GetRoundedPath(control.ClientRectangle, radius); using Pen penBorder = new(borderColor, 1); graph.SmoothingMode = SmoothingMode.AntiAlias; control.Region = new Region(roundPath); graph.DrawPath(penBorder, roundPath);}
private void MainForm_Paint(object sender, PaintEventArgs e){ FormRegionAndBorder(this, borderRadius, e.Graphics, borderColor, borderSize);}
private void MainForm_ResizeEnd(object sender, EventArgs e){ this.Invalidate();}
private void MainForm_SizeChanged(object sender, EventArgs e){ this.Invalidate();}
private void MainForm_Activated(object sender, EventArgs e){ this.Invalidate();}
// Drag and drop the titlebarprivate void panelTitleBar_MouseDown(object sender, MouseEventArgs e){ ReleaseCapture(); SendMessage(this.Handle, 0x112, 0xf012, 0);}
private void MainForm_Resize(object sender, EventArgs e){ this.Invalidate(); panelContainer.Invalidate(); panelSidebar.Invalidate(); panelMainView.Invalidate();}
// Function which actually modifies the UIprivate void panelContainer_Paint(object sender, PaintEventArgs e){ ControlRegionAndBorder(panelContainer, borderRadius - (borderSize / 2), e.Graphics, borderColor);}
#endregionApply this for the rest of the containers - panelLogs panelSidebar and panelMainView
private void panelSidebar_Paint(object sender, PaintEventArgs e){ ControlRegionAndBorder(panelSidebar, 10, e.Graphics, borderColor);}
private void panelLogs_Paint(object sender, PaintEventArgs e){ ControlRegionAndBorder(panelLogs, 10, e.Graphics, borderColor);}
private void panelMainView_Paint(object sender, PaintEventArgs e){ ControlRegionAndBorder(panelMainView, 10, e.Graphics, borderColor);}App - Windows buttons
![]()
// Enumenum ScreenSizeMode{ WithTaskbar, FullScreen, Normal, Minimized}
private ScreenSizeMode _screenSize = ScreenSizeMode.Normal;
// Function for the `middle` buttonprivate void btnMaximize_Click_1(object sender, EventArgs e){ switch (_screenSize) { case ScreenSizeMode.Normal: { _screenSize = ScreenSizeMode.WithTaskbar; if (Screen.PrimaryScreen != null) this.MaximumSize = Screen.PrimaryScreen.WorkingArea.Size; WindowState = FormWindowState.Maximized; btnMaximize.IconChar = IconChar.Expand; break; } case ScreenSizeMode.WithTaskbar: { WindowState = FormWindowState.Normal; if (Screen.PrimaryScreen != null) this.MaximumSize = Screen.PrimaryScreen.Bounds.Size; WindowState = FormWindowState.Maximized; _screenSize = ScreenSizeMode.FullScreen; btnMaximize.IconChar = IconChar.Compress; break; } default: WindowState = FormWindowState.Normal; _screenSize = ScreenSizeMode.Normal; btnMaximize.IconChar = IconChar.Maximize; this.Size = new Size(1280, 720); break; }}
// Function for `minimize` buttonprivate void btnMinimize_Click(object sender, EventArgs e){ WindowState = FormWindowState.Minimized; _screenSize = ScreenSizeMode.Minimized;}
// Function for `close` buttonprivate void btnClose_Click(object sender, EventArgs e){ Application.Exit();}Entity framework (source)
What is Entity Framework?
TLDR;
It is a framework to interact with the database within the C# Project.
Prior to .NET 3.5, we (developers) often used to write ADO.NET code or Enterprise Data Access Block to save or retrieve application data from the underlying database. We used to open a connection to the database, create a DataSet to fetch or submit the data to the database, convert data from the DataSet to .NET objects or vice-versa to apply business rules. This was a cumbersome and error prone process. Microsoft has provided a framework called “Entity Framework” to automate all these database related activities for your application.
Entity Framework is an open-source ORM framework for .NET applications supported by Microsoft. It enables developers to work with data using objects of domain specific classes without focusing on the underlying database tables and columns where this data is stored. With the Entity Framework, developers can work at a higher level of abstraction when they deal with data, and can create and maintain data-oriented applications with less code compared with traditional applications.
Official Definition: “Entity Framework is an object-relational mapper (O/RM) that enables .NET developers to work with a database using .NET objects. It eliminates the need for most of the data-access code that developers usually need to write.”
The following figure illustrates where the Entity Framework fits into your application.
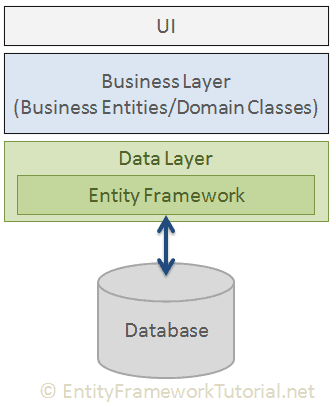
As per the above figure, Entity Framework fits between the business entities (domain classes) and the database. It saves data stored in the properties of business entities and also retrieves data from the database and converts it to business entities objects automatically.
Entity Framework Features
- Cross-platform: EF Core is a cross-platform framework which can run on Windows, Linux and Mac.
- Modelling: EF (Entity Framework) creates an EDM (Entity Data Model) based on POCO (Plain Old CLR Object) entities with get/set properties of different data types. It uses this model when querying or saving entity data to the underlying database.
- Querying: EF allows us to use LINQ queries (C#/VB.NET) to retrieve data from the underlying database. The database provider will translate this LINQ queries to the database-specific query language (e.g. SQL for a relational database). EF also allows us to execute raw SQL queries directly to the database.
- Change Tracking: EF keeps track of changes occurred to instances of your entities (Property values) which need to be submitted to the database.
- Saving: EF executes INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE commands to the database based on the changes occurred to your entities when you call the SaveChanges() method. EF also provides the asynchronous SaveChangesAsync() method.
- Concurrency: EF uses Optimistic Concurrency by default to protect overwriting changes made by another user since data was fetched from the database.
- Transactions: EF performs automatic transaction management while querying or saving data. It also provides options to customize transaction management.
- Caching: EF includes first level of caching out of the box. So, repeated querying will return data from the cache instead of hitting the database.
- Built-in Conventions: EF follows conventions over the configuration programming pattern, and includes a set of default rules which automatically configure the EF model.
- Configurations: EF allows us to configure the EF model by using data annotation attributes or Fluent API to override default conventions.
- Migrations: EF provides a set of migration commands that can be executed on the NuGet Package Manager Console or the Command Line Interface to create or manage underlying database Schema.
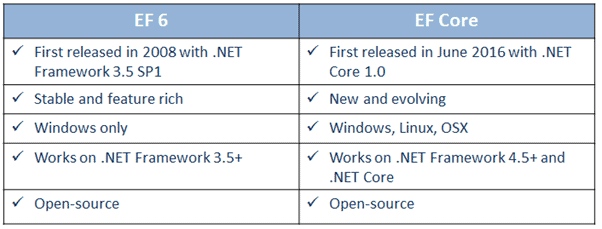
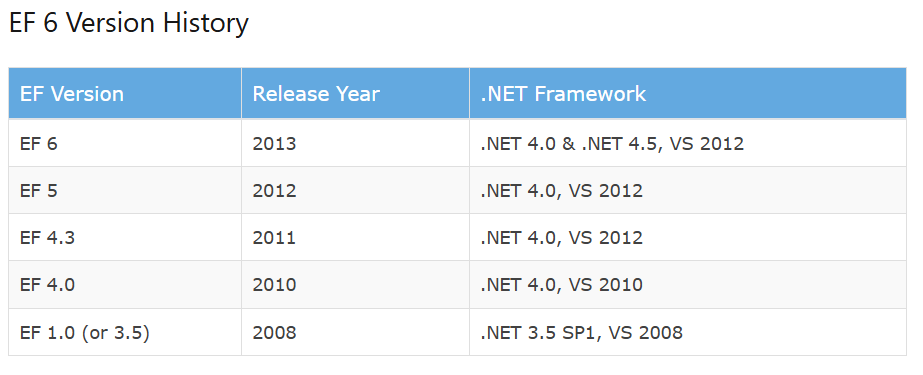
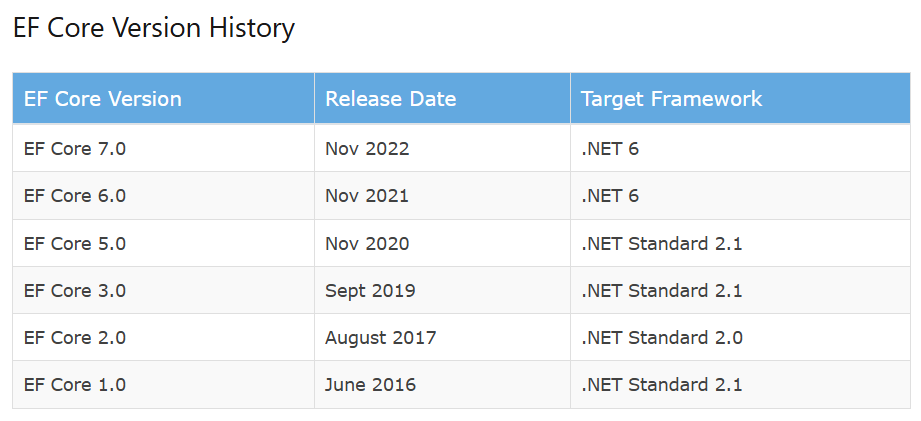
EF Versions and overview
Implementation in project
For a basic implementation, we need a class for an entity and a DbContext to map the entity to the table
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.Schema;using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
namespace Batch.File.Executor.Models;
// Entity class[Table("ExecutionLog")]public class ExecutionLog{ public int Id { get; set; } public DateTime time_start { get; set; } public DateTime time_end { get; set; } public int BatchFileId { get; set; } public BatchFile BatchFile { get; set; }
public override string ToString() => $"Execution ID ({Id}): {time_start} - {time_end}";}
[Table("Log")]public class Log{ public int Id { get; set; } public DateTime LogDate { get; set; } public string Level { get; set; } public string Message { get; set; } public int BatchFileId { get; set; } public BatchFile BatchFile { get; set; }}
[Table("BatchFile")]public class BatchFile{ public int Id { get; set; } public string display_name { get; set; } public DateTime created_at { get; set; } public DateTime? last_modified_at { get; set; } public string text { get; set; } public DateTime? last_executed_at { get; set; } public string? comment { get; set; }
// maps the execution log entries to this particular batch file public ICollection<ExecutionLog> ExecutionLogs { get; set; } = new List<ExecutionLog>();
// maps the log entries to this particular batch file public ICollection<Log> Logs { get; set; } = new List<Log>();}
// DbContext implementationpublic class BatchFileExecutorContext : DbContext{ public BatchFileExecutorContext() { } public BatchFileExecutorContext(DbContextOptions<BatchFileExecutorContext> options) : base(options) { }
// Entities public DbSet<BatchFile> BatchFiles { get; set; }
// Connection Builder protected override void OnConfiguring(DbContextOptionsBuilder? optionsBuilder) { if (optionsBuilder is { IsConfigured: false }) { optionsBuilder.UseSqlite(@"Data Source=batchfileexecutor.db"); } }}- Create and dispose context
// Create a contextvar context = new BatchFileExecutorContext();// Create database, if it does not exist.// If database exists, then this function does have any influence.context.Database.EnsureCreated();// To delete database. WARNING: this will delete the data.context.Database.EnsureDeleted();// Remember to dispose the context after usage.context.Dispose();
- Add and update an Entity - BatchFile
var batchFile = new BatchFile{display_name = $"Batch file {_context.BatchFiles.ToList().Count + 1}",created_at = DateTime.UtcNow,text = "@echo off \n 'Hello world'"};context.BatchFiles.Add(batchFile);context.SaveChanges();
Testing project - Unit.Tests
With unit-tests, each line of production code is tested. Atleast that is the idea for it.
xUnit homepage
xUnit.net is a free, open source, community-focused unit testing tool for the .NET Framework. Written by the original inventor of NUnit v2, xUnit.net is the latest technology for unit testing C#, F#, VB.NET and other .NET languages. xUnit.net works with ReSharper/Rider, CodeRush, TestDriven.NET and Xamarin. It is part of the .NET Foundation, and operates under their code of conduct. It is licensed under Apache 2 (an OSI approved license).
I used xUnit testing framework. It is simple yet powerful to use features made easy it.
3 Basic blocks of each test.
Arrange- Setup the environment and conditions for the test. Eg. mock values, demo data and so on.Act- Here the actual code for testingAssert- Check if the desired condition is reached
Data models for testing
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.Schema;using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
namespace Unit.Tests.Models;
[Table("BatchFile")]public class BatchFile{ public int Id { get; set; } public string display_name { get; set; } public DateTime created_at { get; set; } public DateTime? last_modified_at { get; set; } public string text { get; set; } public DateTime? last_executed_at { get; set; } public string? comment { get; set; }
public ICollection<ExecutionLog> ExecutionLogs { get; set; } = new List<ExecutionLog>(); public ICollection<Log> Logs { get; set; } = new List<Log>();}
[Table("ExecutionLog")]public class ExecutionLog{ public int Id { get; set; } public DateTime time_start { get; set; } public DateTime time_end { get; set; } public int BatchFileId { get; set; } public BatchFile BatchFile { get; set; }
public override string ToString() => $"Execution ID ({Id}): {time_start} - {time_end}";}[Table("Log")]public class Log{ public int Id { get; set; } public DateTime LogDate { get; set; } public string Level { get; set; } public string Message { get; set; } public int BatchFileId { get; set; } public BatchFile BatchFile { get; set; }}
public class BatchFileExecutorContext : DbContext{ public BatchFileExecutorContext() { } public BatchFileExecutorContext(DbContextOptions<BatchFileExecutorContext> options) : base(options) { }
// Entities public DbSet<BatchFile> BatchFiles { get; set; } public DbSet<ExecutionLog> ExecutionLogs { get; set; } public DbSet<Log> Logs { get; set; }
// Connection Builder protected override void OnConfiguring(DbContextOptionsBuilder? optionsBuilder) { if (optionsBuilder is { IsConfigured: false }) { optionsBuilder.UseSqlite(@"Data Source=batchfileexecutor.db"); } }}Below are few tests for the this project
Test - Create an entry in the exceution log table
[Fact]public void CreateAnEntryInTableExecutionLog(){ //Arrange ExecutionLog? dummy = null; var startTime = DateTime.UtcNow.AddDays(-2);
var executionLog = new ExecutionLog() { time_start = startTime, time_end = DateTime.UtcNow, BatchFileId = 1 };
_context.ExecutionLogs.Add(executionLog); _context.SaveChanges();
//Act dummy = _context.ExecutionLogs.FirstOrDefault();
//Assert Assert.NotNull(dummy); _testOutputHelper.WriteLine(dummy.ToString()); Assert.Equal(startTime, dummy.time_start);}Test - Create an entry in the log table
[Fact]public void CreateALogTableEntry(){ var context = new BatchFileExecutorContext(); var batchFileId = context.BatchFiles.ToList().Count + 1; var batchFile = new BatchFile { display_name = $"Batch file {batchFileId}", created_at = DateTime.UtcNow, text = "@echo off \n 'Hello world'" };
var logEntry1 = new Log() { Level = "INFO", LogDate = DateTime.UtcNow, Message = "This is info text" }; batchFile.Logs.Add(logEntry1);
context.BatchFiles.Add(batchFile); context.SaveChanges();}