Generate XML file from Excel using Pandas
Introduction
Today I am came across a task, which required me to generate few XML files. I asked myself, whether I want to spend hours manually creating these XML files or why not automate with 🐍 python and excel.
The charm about using excel is that it gives a better overview of the data. (atleast in my case). Now combined with this thought, need to come about a strategy on deciding the schema for the excel table.
This is what the whole blog is about, generation of xml files based on data from excel file.
Prerequisite
- Excel (or Libre Office)
- Python environment (preferrably VENV)
Setup and inital scripts
-
In the python environment install the packages. Using
poetryexecute the following commands# Setup an environmentpoetry init# Add the packagespoetry add pandas openpyxl lxml -
The final folder structure should look like Below
Directorydocs
- Persons.xlsx
Directorysource
- person.xml
- person.xsd
Directoryscripts
- create_xml_from_excel.py
- validator.py
- .gitignore
- pyproject.toml
Dataflow diagram
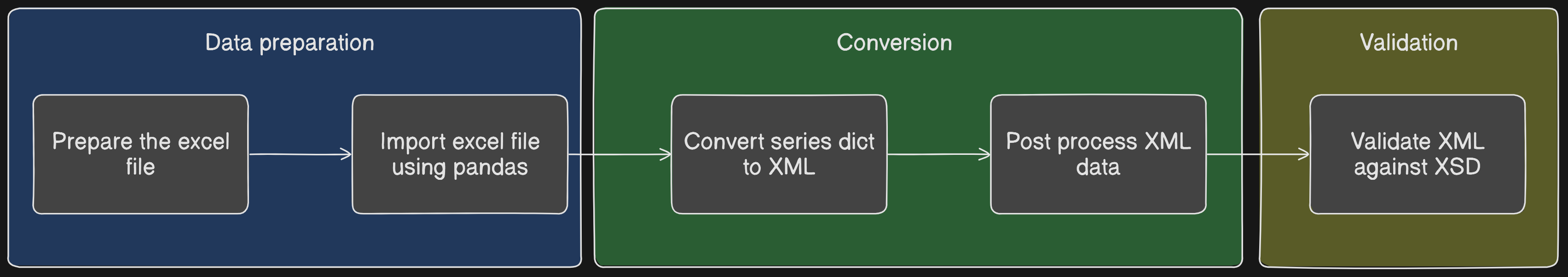
Workflow
A XSD file defines the schema for a xml file. If it exists, then it makes the job of creating the excel file simpler.
Excel file preparation is the first step. Checkout data prepration section
Implementation
Data prepration - Excel file
Sample excel file data
| Attributes | key | Person 1 | Person 2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CREATED | FALSE | FALSE | |||
| personalInfo | name | personalInfo.name | John Doe | Jane Doe | |
| personalInfo | personalInfo.email | john.doe@example.com | jane.doe@example.com | ||
| personalInfo | address.houseNumber | personalInfo.address.houseNumber | 123 | 155 | |
| personalInfo | address.city | city | personalInfo.address.city | Sample City | Test-city |
| personalInfo | address.pincode | pincode | personalInfo.address.pincode | 123456 | 987546 |
| household | children | household.children | Alice,Bob | Charlie,Devil | |
| household | married | household.married | yes | no | |
| household | partner | age | household.partner@age | 32 | 99 |
| household | partner | name | household.partner@name | Jane Doe | Johnny Boy |
Scripts to Data Import and Processing
Create create_xml_from_excel.py in scripts folder
from lxml import etreeimport pandas as pdimport jsonimport osfrom xml.dom.minidom import parseStringimport xml.etree.ElementTree as ETfrom validator import validate_xml
def unflatten_json(flat_json): unflattened = {} for key, value in flat_json.items(): if key == "CREATED": continue parts = key.split(".") data = unflattened for part in parts[:-1]: element, *attr = part.split("@") if element not in data: data[element] = {} data = data[element] if attr: attr_name = attr[0] if '@attributes' not in data: data['@attributes'] = {} data['@attributes'][attr_name] = value
last_element, *last_attr = parts[-1].split("@") if last_attr: if last_element not in data: data[last_element] = {} if '@attributes' not in data[last_element]: data[last_element]['@attributes'] = {} data[last_element]['@attributes'][last_attr[0]] = value else: data[last_element] = value
return unflattened
def create_xml_from_series_dict(json_data, name, ns, schema_location):
# Function to convert dictionary to XML with custom rules def custom_dict_to_xml(data, root_name, namespace): def convert_dict_to_xml_recurse(parent, dict_item): for key, value in dict_item.items(): if key == '@attributes': # If the dictionary contains attributes for attr_key, attr_value in value.items(): parent.setAttribute(attr_key, str(attr_value)) continue
child = doc.createElement(key)
# If the dictionary contains sub-elements if isinstance(value, dict): # Check if the sub-dictionary has attributes if '@attributes' in value: convert_dict_to_xml_recurse( child, {'@attributes': value.pop('@attributes')})
# Recursively convert the rest of the elements convert_dict_to_xml_recurse(child, value) else: # Add text node for simple key-value pairs child.appendChild(doc.createTextNode(str(value)))
parent.appendChild(child)
# Create XML document doc = parseString('<{}></{}>'.format(root_name, root_name)) root = doc.documentElement root.setAttribute("xmlns", namespace)
convert_dict_to_xml_recurse(root, data) print("JSON dict converted to XML document") return doc.toprettyxml()
# Convert JSON to dictionary data_dict = json.loads(json.dumps(json_data))
# Convert dictionary to XML with custom rules xml_data = custom_dict_to_xml(data_dict, 'person', ns)
# Sample function - convert text string with seperator to sequence elements def process_children(xml_string, sep=","): # Parse the XML string root = etree.fromstring(xml_string) namespace = {'ns': ns}
# Navigate to the Children node children = root.find('.//ns:household/ns:children', namespaces=namespace)
# Split the text content into individual child names names = children.text.split(sep)
# Clear the original text content children.clear()
# Add new child elements for name in names: new_element = etree.SubElement(children, 'child') new_element.set('name', name.strip())
# Add xmlns:xsi and xsi:schemaLocation attributes to the root element root.set("{http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance}schemaLocation", f"{ns} ../{schema_location}")
# Convert the modified XML back to a string modified_xml = etree.tostring( root, pretty_print=True, xml_declaration=True, encoding='UTF-8').decode('UTF-8') return modified_xml
xml_data = process_children(xml_data) print("Process 'children' element completed")
if not os.path.exists("converted"): os.makedirs("converted") print("Created the folder 'converted'")
# Save XML data to a file with open(f"converted/{name}.xml", "w") as f: f.write(xml_data) print(f"XML file for person: {name} created!")
df = pd.read_excel("docs/Persons.xlsx", index_col=3)df_modified = df.drop(columns=['Unnamed: 0', 'Unnamed: 1', 'Attributes'])
for col in df_modified.columns: if not df_modified[col]["CREATED"] == True: flat_dict = df_modified[col].dropna() json_data = unflatten_json(flat_dict) name = flat_dict["personalInfo.name"] create_xml_from_series_dict(json_data, name, "http://www.example.com/person", "../source/person.xsd") validate_xml(f"converted/{name}.xml", "source/person.xsd")Create validate.py in scripts folder
from lxml import etree
def validate_xml(filepath, schema_location): # Load the XML and XSD files xml_file = filepath xsd_file = schema_location
with open(xml_file, 'rb') as xml: xml_content = xml.read()
with open(xsd_file, 'rb') as xsd: xsd_content = xsd.read()
# Parse the XML and XSD xml_doc = etree.XML(xml_content) xsd_doc = etree.XMLSchema(etree.XML(xsd_content))
# Validate the XML against the XSD is_valid = xsd_doc.validate(xml_doc)
if is_valid: print(f"The XML document {filepath} is valid.") else: print(f"The XML document {filepath} is invalid.") for error in xsd_doc.error_log: print(error.message)Executing the script
# activate the poetry environmentpoetry shell
python scripts/create_xml_from_excel.py(optional) Extending the scripts as a module including a logger
To make the script more organised and a introducing a better logger, update the files like below.
import loggingimport jsonimport osimport refrom lxml import etreefrom xml.dom.minidom import parseString, Documentimport xml.etree.ElementTree as ET from logger import log_message, setup_logger
LOGGER = setup_logger("create-xml", logging.DEBUG)
def unflatten_json(flat_json): unflattened = {} for key, value in flat_json.items(): if key == "CREATED": continue parts = key.split(".") data = unflattened for part in parts[:-1]: element, *attr = part.split("@") if element not in data: data[element] = {} data = data[element] if attr: attr_name = attr[0] if '@attributes' not in data: data['@attributes'] = {} data['@attributes'][attr_name] = value
last_element, *last_attr = parts[-1].split("@") if last_attr: if last_element not in data: data[last_element] = {} if '@attributes' not in data[last_element]: data[last_element]['@attributes'] = {} data[last_element]['@attributes'][last_attr[0]] = value else: data[last_element] = value
return unflattened
def create_xml_from_series_dict(json_data, name, ns, schema_location):
# Function to convert dictionary to XML with custom rules def custom_dict_to_xml(data, root_name, namespace): def convert_dict_to_xml_recurse(parent, dict_item): for key, value in dict_item.items(): if key == '@attributes': # If the dictionary contains attributes for attr_key, attr_value in value.items(): parent.setAttribute(attr_key, str(attr_value)) continue
child = doc.createElement(key)
# If the dictionary contains sub-elements if isinstance(value, dict): # Check if the sub-dictionary has attributes if '@attributes' in value: convert_dict_to_xml_recurse( child, {'@attributes': value.pop('@attributes')})
# Recursively convert the rest of the elements convert_dict_to_xml_recurse(child, value) else: # Add text node for simple key-value pairs child.appendChild(doc.createTextNode(str(value)))
parent.appendChild(child)
# Create XML document doc = parseString('<{}></{}>'.format(root_name, root_name)) root = doc.documentElement root.setAttribute("xmlns", namespace)
convert_dict_to_xml_recurse(root, data) log_message(LOGGER,logging.DEBUG, "JSON dict converted to XML document") return doc.toprettyxml()
# Convert JSON to dictionary data_dict = json.loads(json.dumps(json_data))
# Convert dictionary to XML with custom rules xml_data = custom_dict_to_xml(data_dict, 'person', ns)
# Sample function - convert text string with seperator to sequence elements def process_children(xml_string, sep=","): # Parse the XML string root = etree.fromstring(xml_string) namespace = {'ns': ns}
# Navigate to the Children node children = root.find('.//ns:household/ns:children', namespaces=namespace)
# Split the text content into individual child names names = children.text.split(sep)
# Clear the original text content children.clear()
# Add new child elements for name in names: new_element = etree.SubElement(children, 'child') new_element.set('name', name.strip())
# Add xmlns:xsi and xsi:schemaLocation attributes to the root element root.set("{http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance}schemaLocation", f"{ns} ../{schema_location}")
# Convert the modified XML back to a string modified_xml = etree.tostring( root, pretty_print=True, xml_declaration=True, encoding='UTF-8').decode('UTF-8') return modified_xml
xml_data = process_children(xml_data) log_message(LOGGER,logging.DEBUG, "Process 'children' element completed")
if not os.path.exists("converted"): os.makedirs("converted") log_message(LOGGER,logging.DEBUG, "Created the folder 'converted'")
# Save XML data to a file with open(f"converted/{name}.xml", "w") as f: f.write(xml_data) log_message(LOGGER,logging.INFO, f"XML file for person: {name} created!") import logging from logger import log_message, setup_loggerfrom lxml import etree
LOGGER = setup_logger("validate-xml", logging.DEBUG)
def validate_xml(filepath, schema_location): # Load the XML and XSD files xml_file = filepath xsd_file = schema_location
with open(xml_file, 'rb') as xml: xml_content = xml.read()
with open(xsd_file, 'rb') as xsd: xsd_content = xsd.read()
# Parse the XML and XSD xml_doc = etree.XML(xml_content) xsd_doc = etree.XMLSchema(etree.XML(xsd_content))
# Validate the XML against the XSD is_valid = xsd_doc.validate(xml_doc)
if is_valid: log_message(LOGGER, logging.INFO, f"The XML document {filepath} is valid.") else: log_message(LOGGER, logging.INFO, f"The XML document {filepath} is invalid.") for error in xsd_doc.error_log: log_message(LOGGER, logging.ERROR, error.message) import logging
def setup_logger(name, level=logging.DEBUG, format='%(asctime)s - %(name)-14s - %(levelname)-8s - %(message)s'): """ Setup a logger with the given name, level, and format.
:param name: Name of the logger. :param level: Logging level (e.g., logging.DEBUG, logging.INFO). :param format: Log message format string. :return: Configured logger. """ logger = logging.getLogger(name) logger.setLevel(level)
# Create a console handler with the specified log level and format ch = logging.StreamHandler() ch.setLevel(level) formatter = logging.Formatter(format) ch.setFormatter(formatter)
# Add the handler to the logger if not logger.hasHandlers(): logger.addHandler(ch)
return logger
def log_message(logger, level, message): """ Log a message with the specified logging level.
:param level: Logging level (e.g., 'DEBUG', 'INFO', 'WARNING', 'ERROR', 'CRITICAL'). :param message: Message to log. """
if isinstance(level, int): # Convert integer level to corresponding string level level = logging.getLevelName(level) elif isinstance(level, str): # Ensure level is in uppercase level = level.upper()
log_func = getattr(logger, level.lower(), None) if log_func: log_func(message) else: raise ValueError(f"Invalid log level: {level}")import pandas as pdfrom create_xml_from_excel import create_xml_from_series_dict, unflatten_jsonfrom validator import validate_xml
NAMESPACE = "http://www.example.com/person"SCHEMA_LOCATION = "source/person.xsd"
if __name__ == "__main__": df = pd.read_excel("docs/Persons.xlsx", index_col=3) df_modified = df.drop(columns=['Unnamed: 0', 'Unnamed: 1', 'Attributes'])
for col in df_modified.columns: if not df_modified[col]["CREATED"] == True: flat_dict = df_modified[col].dropna() json_data = unflatten_json(flat_dict) name= flat_dict["personalInfo.name"] create_xml_from_series_dict(json_data,name, NAMESPACE, SCHEMA_LOCATION) validate_xml(f"converted/{name}.xml", SCHEMA_LOCATION)The folder structure after the update should look below.
Directorydocs
- Persons.xlsx
Directorysource
- person.xml
- person.xsd
Directoryxml_generator
- __main__.py
- create_xml_from_excel.py
- logger.py
- validator.py
- .gitignore
- pyproject.toml

